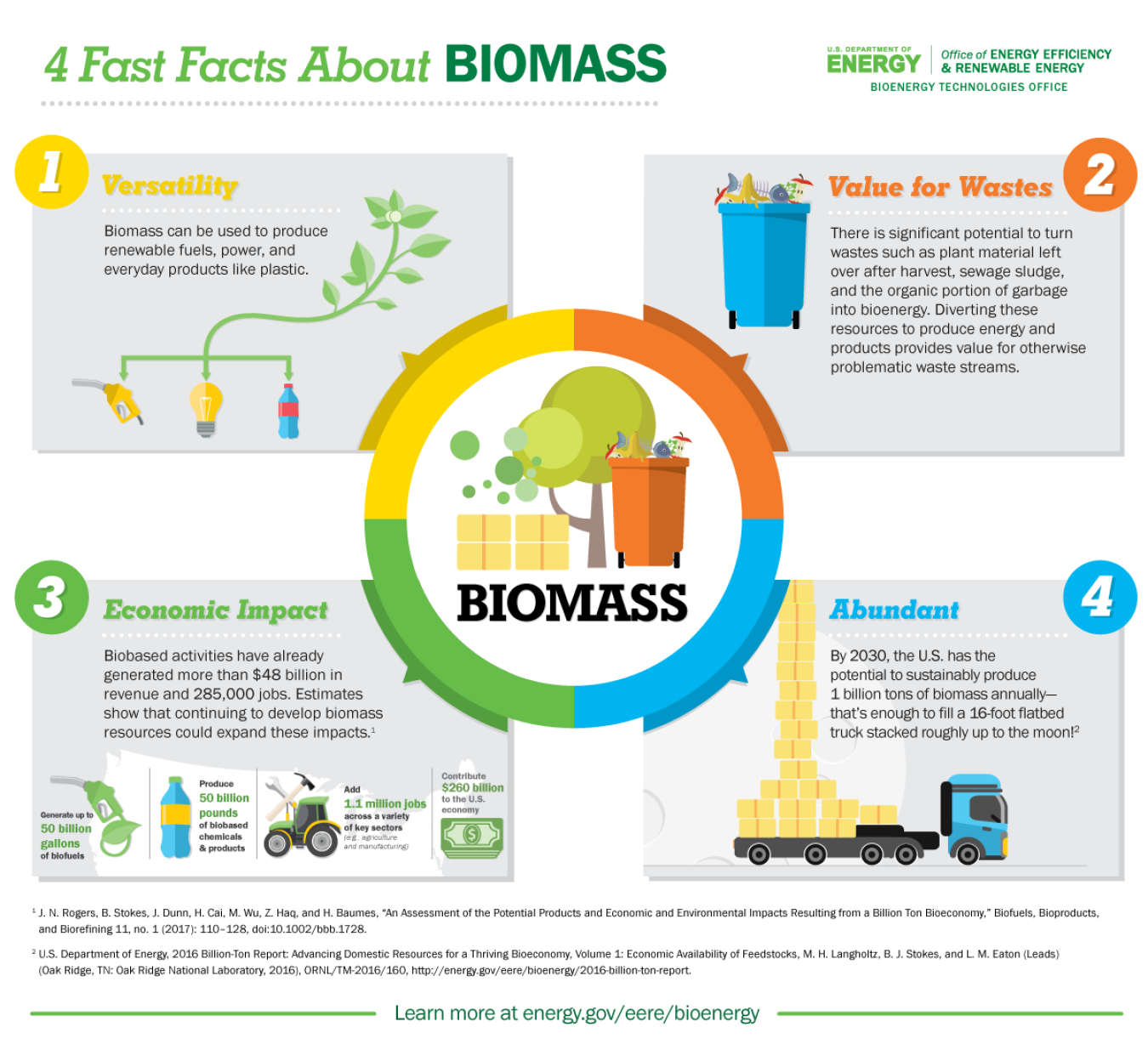
4 Fast Facts About Biomass
Trang thông tin điện tử về Năng lượng sinh khối

Common Questions about Biomass
1. What is biomass energy? - Biomass energy refers to the use of organic materials, such as plants and animal waste, to generate heat and electricity. It is a renewable source of energy that can reduce greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on fossil fuels. 2. How is biomass energy generated? - Biomass energy can be generated through different processes, including combustion, gasification, and anaerobic digestion. In combustion, organic materials are burned to produce heat, which can then be converted into electricity. Gasification involves converting biomass into a mixture of gases, which can be used for heating or electricity production. Anaerobic digestion breaks down organic materials in an oxygen-free environment, producing biogas that can be used as a fuel. 3. What are the advantages of using biomass energy? - Biomass energy has several advantages, including: - Reduction of greenhouse gas emissions: Biomass is considered carbon-neutral since plants absorb carbon dioxide during their growth, offsetting the emissions produced during combustion. - Utilization of waste materials: Biomass energy can make use of agricultural residues, forest residues, and animal waste, reducing the need for landfilling or burning these materials. - Renewable and sustainable: Unlike fossil fuels, biomass is considered a renewable resource as long as it is managed responsibly and the supply is replenished through reforestation and agriculture. - Local economic benefits: Biomass energy production can create local job opportunities and support rural economies. 4. What are the drawbacks of biomass energy? - Despite its advantages, biomass energy also has some drawbacks, including: - Land use concerns: Biomass production requires land, which may compete with other land uses such as food production or conservation. - Air pollution: Combustion of biomass can release pollutants such as nitrogen oxides and particulate matter, although modern technologies can mitigate these emissions. - Transportation and storage challenges: Biomass needs to be transported and stored properly, which can add logistical complexities and costs to its use. - Limited energy density: Biomass has a lower energy density compared to fossil fuels, requiring larger volumes for the same energy output. 5. Is biomass energy sustainable? - Biomass can be a sustainable source of energy if managed properly. It is crucial to ensure that biomass is obtained from responsibly managed sources and that the rate of biomass harvesting does not exceed the rate of biomass regrowth. Good forest management practices, reforestation efforts, and the use of dedicated energy crops can contribute to the sustainability of biomass energy. 6. How does biomass compare to other renewable energy sources? - Biomass energy can complement other renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar power. Unlike wind and solar, biomass can provide a stable, dispatchable energy supply, as it can be stored and used when needed. Additionally, biomass facilities can be operated continuously, providing a consistent energy output. 7. What types of biomass can be used for energy production? - Various types of biomass can be used for energy production, including: - Wood and wood residues - Crop residues (e.g., corn stalks, wheat straw) - Energy crops (e.g., switchgrass, miscanthus) - Agricultural and food processing residues - Animal manure - Algae - Municipal solid waste (MSW) 8. How is biomass energy used in heating? - Biomass energy can be used for heating purposes through direct combustion in stoves, boilers, or furnace systems. Biomass pellets, made from compressed organic materials, can be used as a convenient fuel source for residential and industrial heating. 9. Can biomass energy replace fossil fuels entirely? - While biomass energy has the potential to replace a significant portion of fossil fuels, it is unlikely to completely replace them. Biomass resources have limits, and a diversified energy mix that includes other renewable sources, energy efficiency measures, and transitioning to cleaner fuels is necessary to achieve a sustainable and low-carbon energy future. 10. Are there any environmental concerns associated with biomass energy? - There are some environmental concerns associated with biomass energy, including: - Deforestation: Unsustainable biomass harvesting can contribute to deforestation, biodiversity loss, and habitat degradation. - Soil degradation: Improper biomass harvesting practices can lead to soil erosion and nutrient depletion, affecting agricultural productivity. - Water use: Biomass energy production may require substantial amounts of water for irrigation or processing, which can strain water resources in water-stressed regions. 11. How is biomass energy supported by government policies? - Many governments have implemented policies to support the development and use of biomass energy. These policies can include incentives for biomass production, tax credits for biomass projects, renewable energy targets, and feed-in tariffs to ensure a stable market for biomass-generated electricity. 12. What is the future outlook for biomass energy? - The future of biomass energy looks promising. Technological advancements, such as more efficient combustion systems and biomass conversion technologies, continue to improve the efficiency and sustainability of biomass energy. Biomass may play a significant role in the transition towards a low-carbon and renewable energy future, particularly in sectors that are challenging to decarbonize, such as heating and heavy industries. However, it is essential to balance biomass production with sustainable land management practices and ensure that other renewable energy sources are also utilized.

